처음부터 플러터 프로젝트를 도입하여 안드로이드와 iOS 둘 다 개발하는게 가장 좋지만
대부분의 기업, 사람들은 이미 갖고 있는 프로젝트가 있고 거기에 Flutter나 KMP 같은 하이브리드 개발 방식을 도입할 방법을 찾고 있을거라 생각합니다.
Flutter는 기존 안드로이드, iOS 프로젝트에서 새롭게 Flutter 전용 화면을 넣어서 그 화면에 대한 모든 것은 Flutter로 처리되게 할 수 있는
기술을 지원하고 있습니다.
Add Flutter Screen For Android
https://docs.flutter.dev/add-to-app/android/add-flutter-screen
Add a Flutter screen to an Android app
Learn how to add a single Flutter screen to your existing Android app.
docs.flutter.dev
Android에 대해서는 단순히 screen만 추가하는 것이 아니라
Fragment나 View를 추가할수도 있지만, iOS에서는 Screen 추가만 가능하기 때문에
안드로이드, iOS 둘 다 같은 같은 화면을 추가하고 싶다면 screen 추가만이 유일한 방법입니다.
지금부터 다음과 같은 앱 구조를 갖는 프로젝트를 만들 예정입니다.
(프로젝트 이름은 아무거나 지정해도 상관 없습니다.)

Flutter 프로젝트 만들기
저희는 플러터 프로젝트 자체가 필요한게 아니라 플러터 module이 필요하기 때문에 다음과 같은 커맨드로
플러터 모듈을 생성합니다.
flutter create -t module --org com.example new_feature_flutter_module
그리고 main.dart에 다음과 같은 코드를 넣어줍니다.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
const channelName = 'com.example.module-test/custom';
const methodChannel = MethodChannel(channelName);
void main() => runApp(const MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Module Test',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
routes: {
'/custom1': (context) => const Custom1(title: 'Flutter Custom Module1'),
},
);
}
}
class Custom1 extends StatefulWidget {
const Custom1({super.key, required this.title});
final String title;
@override
State<Custom1> createState() => _Custom1State();
}
class _Custom1State extends State<Custom1> {
int _counter = 0;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
print("new flutter loaded");
}
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Colors.cyanAccent,
leading: IconButton(
icon: const Icon(Icons.arrow_back_ios),
onPressed: () {
SystemNavigator.pop();
},
),
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'Module Test1',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
backgroundColor: Colors.cyanAccent,
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
플러터 부분의 화면 기능은 아주 단순합니다.
가운데 카운트를 해주는 Text Widget이 있고 오른쪽 하단에는 해당 카운트를 늘려주는 Floating Button이 존재합니다.

여기서 중요한 부분은 다음과 같습니다.
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Module Test',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
routes: {
'/custom1': (context) => const Custom1(title: 'Flutter Custom Module1'),
},
);
}
}
routes 라는 부분을 통해 특정 Key가 일치한다면 Custom1이라는 화면을 출력하도록 하고 있습니다.
Flutter에서 화면을 출력할 때 해당 routes를 통해 표시되는 첫 화면을 출력한다는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
이후 Flutter 모듈 프로젝트에서 다음과 같은 커맨드를 실시합니다.
flutter build aar
그럼 다음과 같이 진행되면서 aar 파일을 자동으로 만들어줍니다.

일단 여기까지 만드는데 성공했다면...
다음에는 같은 위치의 디렉토리에 android 프로젝트를 만들어줍니다.
안드로이드 프로젝트 셋업하기

위 그림과 같은 모습이 되게 새로운 안드로이드 프로젝트를 만들어줍니다.
참고로 Compose로 만들어도 괜찮고 일반적인 AndroidView 프로젝트로 해도 상관없습니다.
제일 먼저 해야할 것은 app/build.gradle.kts 부분의 수정입니다.
플러터는 동작할 수 있는 아키텍처가 한정적이기 때문에 동작 가능한 아키텍처를 지정해줘야합니다.
다음 코드를 추가합니다.
app/build.gradle.kts
android {
//...
defaultConfig {
ndk {
// Filter for architectures supported by Flutter
abiFilters += listOf("armeabi-v7a", "arm64-v8a", "x86_64")
}
}
}
settings.gradle.kts
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.PREFER_SETTINGS)
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
maven("https://storage.googleapis.com/download.flutter.io") // 추가
}
}
// 추가
rootProject.name = "new_feature_android"
include(":app")
// Flutter Module 설정
val flutterProjectRoot = rootDir.parentFile
val flutterModuleName = "new_feature_flutter_module"
val flutterModulePath = File(flutterProjectRoot, flutterModuleName)
if (flutterModulePath.exists()) {
val flutterAndroidPath = File(flutterModulePath, ".android")
val includeFlutterScript = File(flutterAndroidPath, "include_flutter.groovy")
if (includeFlutterScript.exists()) {
println("✅ Flutter module exists: $flutterModuleName")
apply(from = includeFlutterScript)
} else {
println("⚠️ Flutter module found but, not initialized.")
println("please run flutter pub get.")
}
} else {
println("⚠️ Flutter module not found: $flutterModuleName")
}
저는 플러터 모듈의 이름을 new_feature_android로 만들었기 때문에 위와 같이 정의했습니다.
다음으로는 AndroidMenifast에 다음과 같은 내용을 추가해줍니다.
AndroidManifest.xml
<activity
android:name="io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterActivity"
android:theme="@style/LaunchTheme"
android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden|keyboard|screenSize|locale|layoutDirection|fontScale|screenLayout|density|uiMode"
android:hardwareAccelerated="true"
android:windowSoftInputMode="adjustResize"
/>
여기까지 하면 Andorid 프로젝트의 셋업은 끝입니다.
이제부터 MainActivity에 실제로 Flutter 화면으로 이동하는 코드를 작성해보겠습니다.
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
companion object {
private const val ENGINE_ID = "new_feature_flutter_module"
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContent {
New_feature_androidTheme {
Surface(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
CenterScreen()
}
}
}
}
private fun createFreshFlutterEngine(): FlutterEngine {
// delete previous FlutterEngine
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().get(ENGINE_ID)?.destroy()
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().remove(ENGINE_ID)
// create a new FlutterEngine
val flutterEngine = FlutterEngine(this)
// Dart run
flutterEngine.dartExecutor.executeDartEntrypoint(
DartExecutor.DartEntrypoint.createDefault()
)
// Store the FlutterEngine in the cache
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().put(ENGINE_ID, flutterEngine)
return flutterEngine
}
private fun openFlutterScreen() {
createFreshFlutterEngine()
// Flutter 모듈에서 정한 cumstom1 이라는 이름의 경로를 지정
val intent = FlutterActivity
.withNewEngine()
.initialRoute("/custom1")
.build(this)
startActivity(intent)
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().get(ENGINE_ID)?.destroy()
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().remove(ENGINE_ID)
}
@Composable
fun CenterScreen() {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center
) {
Text(
text = "Android",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineLarge,
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary,
modifier = Modifier.padding(bottom = 24.dp)
)
Row(
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(16.dp),
modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 32.dp)
) {
Button(
onClick = {
openFlutterScreen()
}
) {
Text("Move to Flutter")
}
}
}
}
}
이를 실행하면 다음과 같이 동작하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
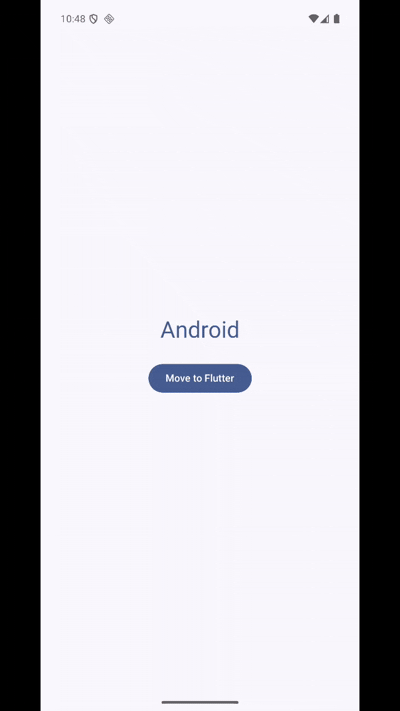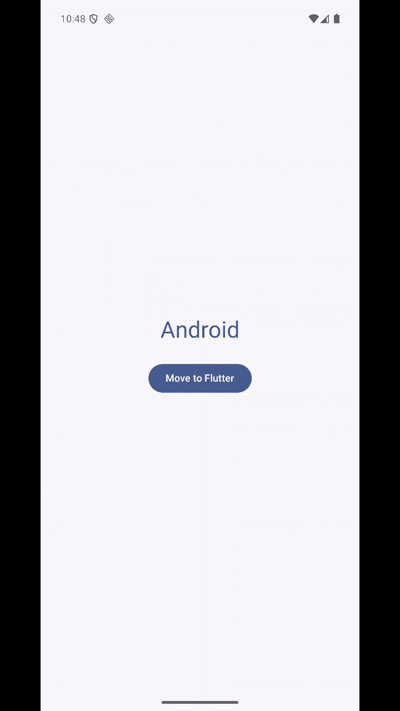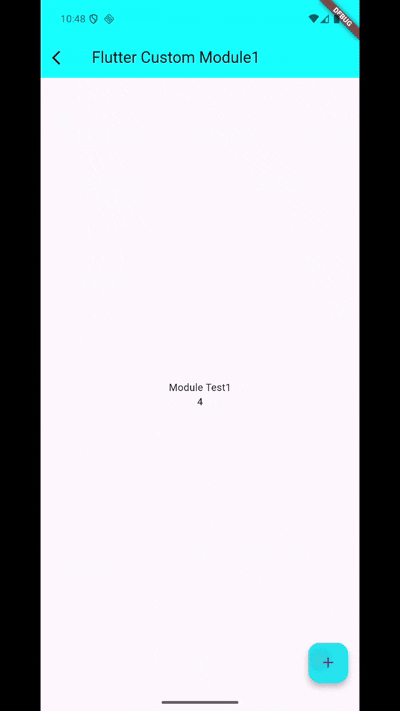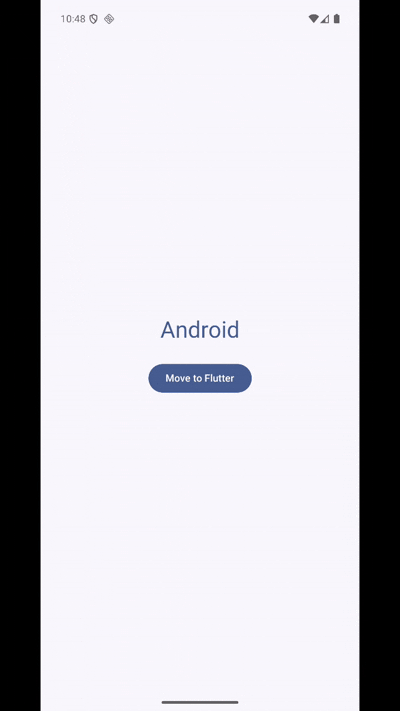
Flutter 엔진 캐싱하기
위 결과를 보면 Move To Flutter 버튼을 클릭하고 나서 Flutter 화면으로 넘어가기 까지 1초가 넘는 시간이 걸린다는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
실제로 앱을 사용하는데 이러한 현상이 발생한다면 사용자는 앱이 멈춘건가? 라고 생각할 수 있습니다.
이는 FlutterActivty를 실행할 때 Flutter Engine을 초기화 해야하는데.
Flutter Engine을 초기화하는데 시간이 오래 걸리기 때문입니다.
이를 방지하기 위해 Caching 처리를 해서 Flutter Engine을 미리 초기화할 수 있습니다.
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
companion object {
private const val ENGINE_ID = "new_feature_flutter_module"
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
// 앱을 시작하자마자 플러터 엔진 초기화
createFreshFlutterEngine()
setContent {
New_feature_androidTheme {
Surface(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
CenterScreen()
}
}
}
}
private fun createFreshFlutterEngine(): FlutterEngine {
// delete previous FlutterEngine
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().get(ENGINE_ID)?.destroy()
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().remove(ENGINE_ID)
// create a new FlutterEngine
val flutterEngine = FlutterEngine(this)
// 플러터 화면의 경로를 네비게이션으로 지정하도록 변경
flutterEngine.navigationChannel.setInitialRoute("/custom1")
// Dart run
flutterEngine.dartExecutor.executeDartEntrypoint(
DartExecutor.DartEntrypoint.createDefault()
)
// Store the FlutterEngine in the cache
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().put(ENGINE_ID, flutterEngine)
return flutterEngine
}
private fun openFlutterScreen() {
// 캐싱된 플러터 엔진을 사용하도록 변경
val intent = FlutterActivity
.withCachedEngine(ENGINE_ID)
.build(this)
startActivity(intent)
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().get(ENGINE_ID)?.destroy()
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().remove(ENGINE_ID)
}
@Composable
fun CenterScreen() {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center
) {
Text(
text = "Android",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineLarge,
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary,
modifier = Modifier.padding(bottom = 24.dp)
)
Row(
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(16.dp),
modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 32.dp)
) {
Button(
onClick = {
openFlutterScreen()
}
) {
Text("Move to Flutter")
}
}
}
}
}
이전 코드에서 다음과 같은 부분을 변경했습니다.
- 앱을 실행했을 때 플러터 엔진을 초기화 하도록 변경
- 플러터 모듈의 화면으로 넘어갈 때 캐싱된 플러터 엔진을 사용하도록 변경
- 초기 경로를 navigationChannel을 사용해서 지정하도록 변경
이렇게 설정하면 기존 버전보다 훨씬 빠르게 화면 전환이 이루어지는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Flutter로 화면 전환할 때 데이터도 같이 넘겨주기
지금까지 알아본 것에 의하면 다음과 같은 것들을 할 수 있다는 것을 알게되었습니다.
- 안드로이드 프로젝트에서 원하는 플러터 화면 열기
- 플러터 엔진을 미리 캐싱하여 플러터로의 화면 전환을 빠르게 하기
마지막으로 중요한 것이 안드로이드 프로젝트로 플러터 화면을 열 때 테이더도 같이 전송하는 것입니다.
Flutter로 화면 전환할 때 데이터도 같이 넘겨주기 - 안드로이드 앱 셋팅
일반적으로 안드로이드에서 데이터를 받고 가공을 하기 위해 data class를 주로 사용하기 때문에
여기서도 같은 예시로 사용해 보겠습니다.
다음과 같이 예시로 사용할 UserInfo 데이터를 생성합니다.
UserInfo.kt
data class UserInfo(
val id: String,
val name: String,
val email: String,
val profilePictureUrl: String? = null
) {
fun toMap(): Map<String, Any?> {
return mapOf(
"id" to id,
"name" to name,
"email" to email,
"profilePictureUrl" to profilePictureUrl
)
}
companion object {
fun getDummyUserList(): List<UserInfo> = listOf(
UserInfo("1", "John Doe", "john.doe@example.com", "https://example.com/profile/john.jpg"),
UserInfo("2", "Jane Smith", "jane.smith@example.com", "https://example.com/profile/jane.jpg"),
UserInfo("3", "Kim", "chulsoo.kim@example.com", "https://example.com/profile/chulsoo.jpg"),
UserInfo("4", "Lee", "younghee.lee@example.com", null),
UserInfo("5", "Park", "jimin.park@example.com", "https://example.com/profile/jimin.jpg")
)
}
}
그리고 나서 MainActivity에 다시 해당 데이터를 넘겨주는 작업을 실시합니다.
package com.example.new_feature_android
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.activity.ComponentActivity
import androidx.activity.compose.setContent
import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Arrangement
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Row
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding
import androidx.compose.material3.Button
import androidx.compose.material3.MaterialTheme
import androidx.compose.material3.Surface
import androidx.compose.material3.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import com.example.new_feature_android.models.UserInfo
import com.example.new_feature_android.ui.theme.New_feature_androidTheme
import io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterActivity
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngine
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngineCache
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.dart.DartExecutor
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
companion object {
private const val ENGINE_ID = "new_feature_flutter_module"
private const val CHANNEL = "com.example.new_feature_android/custom1"
}
private var methodChannel: MethodChannel? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
createFreshFlutterEngine()
setContent {
New_feature_androidTheme {
Surface(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
CenterScreen()
}
}
}
}
private fun createFreshFlutterEngine(): FlutterEngine {
// delete previous FlutterEngine
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().get(ENGINE_ID)?.destroy()
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().remove(ENGINE_ID)
// create a new FlutterEngine
val flutterEngine = FlutterEngine(this)
// set Flutter screen native route
flutterEngine.navigationChannel.setInitialRoute("/custom1")
// MethodChannel setup
setupMethodChannel(flutterEngine)
// Dart run
flutterEngine.dartExecutor.executeDartEntrypoint(
DartExecutor.DartEntrypoint.createDefault()
)
// Store the FlutterEngine in the cache
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().put(ENGINE_ID, flutterEngine)
return flutterEngine
}
private fun setupMethodChannel(flutterEngine: FlutterEngine) {
methodChannel = MethodChannel(flutterEngine.dartExecutor.binaryMessenger, CHANNEL)
methodChannel?.setMethodCallHandler { call, result ->
when (call.method) {
"getUserInfo" -> {
try {
val userList = UserInfo.getDummyUserList()
val userMaps = userList.map { it.toMap() }
result.success(userMaps)
} catch (e: Exception) {
result.error("ERROR", "Failed to get user info", e.message)
}
}
"getCurrentUser" -> {
try {
val currentUser = UserInfo.getDummyUserList().first()
result.success(currentUser.toMap())
} catch (e: Exception) {
result.error("ERROR", "Failed to get current user", e.message)
}
}
else -> {
result.notImplemented()
}
}
}
}
private fun openFlutterScreen() {
val intent = FlutterActivity
.withCachedEngine(ENGINE_ID)
.build(this)
startActivity(intent)
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().get(ENGINE_ID)?.destroy()
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().remove(ENGINE_ID)
}
@Composable
fun CenterScreen() {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center
) {
Text(
text = "Android",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineLarge,
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary,
modifier = Modifier.padding(bottom = 24.dp)
)
Row(
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(16.dp),
modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 32.dp)
) {
Button(
onClick = {
// Flutter 화면을 열기 전에 사용자 정보를 전송
openFlutterScreen()
}
) {
Text("Move to Flutter")
}
}
}
}
}
위 코드에서 중요한 부분은 다음과 같습니다.
1. 메시지 채널 셋업
- setupMethodChannel(flutterEngine)
2. 특정 채널의 이름으로 메시지 채널을 만든다.
- MethodChannel(flutterEngine.dartExecutor.binaryMessenger, CHANNEL)
3. 플러터쪽에서 보내는 메시지 채널 수신 핸들러
- methodChannel?.setMethodCallHandler
- 플러터쪽에서 메시지 채널로 호출을 하면 해당 함수에서 받아서 처리합니다
Flutter로 화면 전환할 때 데이터도 같이 넘겨주기 - 플러터 모듈 셋팅
다음으로 플러터 모듈에서는 다음과 같은 두 개의 작업을 추가해야합니다.
- Flutter 화면이 열렸을 때 Android 앱에 데이터를 보내라는 신호 넣기
- 데이터를 실제로 받았을 때 수신 처리
먼저 안드로이드와 똑같이 UserInfo.dart 파일을 만들어 줍니다.
UserInfo.dart
class UserInfo {
final String id;
final String name;
final String email;
final String? profilePictureUrl;
const UserInfo({
required this.id,
required this.name,
required this.email,
this.profilePictureUrl,
});
// Android에서 보낸 Map 데이터를 UserInfo로 변환
factory UserInfo.fromMap(Map<String, dynamic> map) {
return UserInfo(
id: map['id'] ?? '',
name: map['name'] ?? '',
email: map['email'] ?? '',
profilePictureUrl: map['profilePictureUrl'],
);
}
// UserInfo를 Map으로 변환 (필요시 사용)
Map<String, dynamic> toMap() {
return {
'id': id,
'name': name,
'email': email,
'profilePictureUrl': profilePictureUrl,
};
}
@override
String toString() {
return 'UserInfo{id: $id, name: $name, email: $email, profilePictureUrl: $profilePictureUrl}';
}
}
그리고 main.dart에서 안드로이드 쪽에 신호를 보내고 수신 하는 부분을 넣어줍니다.
main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'models/UserInfo.dart';
// 채널명을 Android에서 지정한 것과 일치시켜야함
const channelName = 'com.example.new_feature_android/custom1';
const methodChannel = MethodChannel(channelName);
void main() => runApp(const MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Module Test',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
routes: {
'/custom1': (context) => const Custom1(title: 'Flutter Custom Module1'),
},
);
}
}
class Custom1 extends StatefulWidget {
const Custom1({super.key, required this.title});
final String title;
@override
State<Custom1> createState() => _Custom1State();
}
class _Custom1State extends State<Custom1> {
int _counter = 0;
List<UserInfo> _userList = [];
UserInfo? _currentUser;
bool _isLoading = false;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
print("new flutter loaded");
_setupMethodChannel();
_loadUserData();
}
void _setupMethodChannel() {
// Android에서 보내는 데이터를 받는 리스너
methodChannel.setMethodCallHandler((call) async {
switch (call.method) {
case 'receiveUserInfo':
_handleReceiveUserInfo(call.arguments);
break;
default:
print('Unknown method: ${call.method}');
}
});
}
void _handleReceiveUserInfo(dynamic arguments) {
if (arguments is List) {
setState(() {
_userList = arguments
.map((userMap) => UserInfo.fromMap(Map<String, dynamic>.from(userMap)))
.toList();
});
print('Received ${_userList.length} users from Android');
}
}
// Android에서 사용자 데이터 요청
Future<void> _loadUserData() async {
setState(() => _isLoading = true);
try {
// 전체 사용자 리스트 요청
final result = await methodChannel.invokeMethod('getUserInfo');
if (result is List) {
setState(() {
_userList = result
.map((userMap) => UserInfo.fromMap(Map<String, dynamic>.from(userMap)))
.toList();
});
}
// 현재 사용자 요청
final currentUserResult = await methodChannel.invokeMethod('getCurrentUser');
if (currentUserResult is Map) {
setState(() {
_currentUser = UserInfo.fromMap(Map<String, dynamic>.from(currentUserResult));
});
}
print('Loaded ${_userList.length} users');
print('Current user: ${_currentUser?.name}');
} catch (e) {
print('Error loading user data: $e');
} finally {
setState(() => _isLoading = false);
}
}
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Colors.cyanAccent,
leading: IconButton(
icon: const Icon(Icons.arrow_back_ios),
onPressed: () {
SystemNavigator.pop();
},
),
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: _isLoading
? const Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator())
: SingleChildScrollView(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'Module Test1',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 24, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
Text(
'Counter: $_counter',
style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
const SizedBox(height: 32),
// 현재 사용자 정보 표시
if (_currentUser != null) ...[
const Text(
'Current User:',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
Card(
child: ListTile(
leading: _currentUser!.profilePictureUrl != null
? CircleAvatar(
backgroundImage: NetworkImage(_currentUser!.profilePictureUrl!),
)
: const CircleAvatar(child: Icon(Icons.person)),
title: Text(_currentUser!.name),
subtitle: Text(_currentUser!.email),
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 32),
],
// 전체 사용자 리스트 표시
const Text(
'All Users:',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
ListView.builder(
shrinkWrap: true,
physics: const NeverScrollableScrollPhysics(),
itemCount: _userList.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final user = _userList[index];
return Card(
child: ListTile(
leading: user.profilePictureUrl != null
? CircleAvatar(
backgroundImage: NetworkImage(user.profilePictureUrl!),
)
: const CircleAvatar(child: Icon(Icons.person)),
title: Text(user.name),
subtitle: Text(user.email),
trailing: Text('ID: ${user.id}'),
),
);
},
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
backgroundColor: Colors.cyanAccent,
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
위 코드에서 중요한 것은 다음과 같습니다.
1. 안드로이드 쪽에서 정의한 채널 이름과 동일한 채널 이름 사용하기
- const channelName = 'com.example.new_feature_android/custom1';
- const methodChannel = MethodChannel(channelName);
2. Android에 사용자 데이터 요청
- _loadUserData()
3. Android에서 받은 데이터를 수신하여 처리
- _setupMethodChannel()

'플러터(flutter)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| FlutterFire CLI 사용해서 Flutter에서 Flavor 나누기 (2) | 2025.06.28 |
|---|---|
| 플러터로 만든 안드로이드 앱 스토어에 릴리즈(Release) 하기 (0) | 2025.01.13 |
| [플러터] flutter_launcher_icons를 사용해서 앱 아이콘 넣기(자세히 설명) (1) | 2024.12.22 |
| 플러터에 Firebase 넣고 초기화 하는 방법(feat. 초보자 가이드) (2) | 2024.12.14 |
| 플러터에서 Flavor를 사용해서 iOS 개발 환경 분리 및 변수 설정 (1) | 2024.12.11 |
"이 포스팅은 쿠팡 파트너스 활동의 일환으로, 이에 따른 일정액의 수수료를 제공받습니다."





댓글